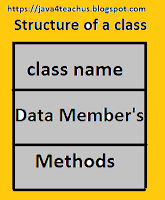
In previous post we have already learnt about on the Syntax of a class. But we would like known about the program of class syntax.
Q. Write a class definition for computing subtraction of two number?
program
class Sub{
int a, b, c ;
void accept( )
{
a=40;
b=30;
}
void add( )
{
int c=a-b;
}
void display( )
{
System.out.println(“value of a="+a);
System.out.println(“value of b=”+b);
System.out.println(“sub=”+c);
}
}
Q . Write a class definition for computing multiplication of three number?.
program
class Multiplication{
int a, b, c ,d ;
void accept( )
{
a=30;
b=60;
c=30
}
void mul( )
{
d= a*b*c;
}
void display( )
{
System.out.println(“value of a="+a);
System.out.println(“value of b=”+b);
System.out.println("value of c=" +d);
System.out.println(“Mul=”+c);
}
}
Q . Write a class definition for computing (a+b)2?
program
class Sqr
{
int a,b,c;
void accept()
{
a=10;
b=20;
}
void sqr()
{
c=a*a+b*b+2*a*b;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println(“value of a="+a);
System.out.println(“value of b="+b);
System.out.println(“square="=c);
}
}
Q . Write a class definition for computing a 2 ?
program
class Square
{
int a,b;
void accept()
{
a=10;
}
void square()
{
b=a*a;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println(“value of a="+a);
System.out.println(“square="+b);
}
}
Q . Write a class definition for computing area of triangle ?
program
{
int b,h;
float i;
void accept()
{
b=1;
h=2;
}
void triangle()
{
i=0.5*b*h;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println(“value of b="+b);
System.out.println(“value of h="+h);
System.out.println(“area of triangle="+i);
}
Q. Write a class definition for computing area of circle ?.
program
class AreaOfCircle
{
int r;
double pi,s;
void accept()
{
r=10;
pi=3.14;
}
void circle()
{
s=pi*r*r;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println(“value of r="+r);
System.out.println(“area of circle="+s);
}
}
Q. Write a class definition for computing area of Rectangle ?.
program
class AreaOfRectangle
{
int a,l,b;
void accept()
{
l=100;
b=200;
}
void areaOfRectangle()
{
a=l*b;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println(“value of l="+l);
System.out.println(“value of b="+b);
System.out.println(“areaofrectangle="+a);
}
}
{
int a,l,b;
void accept()
{
l=100;
b=200;
}
void areaOfRectangle()
{
a=l*b;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println(“value of l="+l);
System.out.println(“value of b="+b);
System.out.println(“areaofrectangle="+a);
}
}
Q. Write a class definition for computing the circumstance of circle ?.
program
class CircumferenceOfCircle
{
int r;
double pi,c;
void accept()
{
pi=3.14;
r=20;
}
void circumferenceOfCircle()
{
c=2*pi*r;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println("value of r="+r);
System.out.println("value of pi="+pi);
System.out.println("CircumferenceOfCircle="+c);
}
}
Q. Write a class definition for computing the Volume of a cube?.
program
class VolumeOfCube
{
int b,h,v;
void accept()
{
b=1;
h=2;
}
void volumeOfCube()
{
v=b*h;
}
void display()
{
}
}
{
v=b*h;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println("value of b="+b);
System.out.println("value of h="+h);
System.out.println("VolumeOfCube="+v);
}
Q .Write a java with class definition for computing sum of two number?
program
class Sum
{
int a, b, c ;
void accept()
{
a=10;
b=20;
}
void add( )
{
int c=a+b;
}
void display( )
{
System.out.println (“value of a="+a);
System.out.println (“value of b=”+b);
System.out.println(“sum =”+c);
}
}
In the above program, Whenever we write the java program then we must have to define the class name by using the keyword called as "class". Here the class name what we defined that is Sum.
A logic of the above program is c= a+b. Here a,b are the two input variables which is used to store the values and c is the output variable of a java program.
accept(), add(), display() are the methods which is always shows Business Logic of a java program.