Inheritance
Introduction
Inheritance is one of the main features of OOPS and makes it is development reusable.
Definition
The processes of obtaining data members & methods (features) from one class to another class is called inheritance. (or) The process of deriving the one class features into another class is called as inheritance.
The processes of obtaining data members & methods (features) from one class to another class is called inheritance. (or) The process of deriving the one class features into another class is called as inheritance.
Super Class and Base Class
The class which is giving the data members & methods is called "Base class / super class/ parent class". where the class is taking data members & methods is called as “Derived class / Child class”.
Inheritance concept always follows logical memory management. This management is base class features are available in derived class without taking any physical and without taking physical code (in the content of we can just reuse the features of base class).
Inheritance concept is also known as re-usability (or) extended class (or) derivation (or) sub class.
Advantages / Benefits Of Inheritance
If we develop any Java application in inheritance concept we get the following advantages.
- Application memory space is less.
- Application development time is less.
- Application execution time is less.
- Application performance is improved.
- Redundancy of code is minimized.
- Able to get the slogan of Java.
Types of Inheritance (or) Re-Usability Techniques
A pattern or model which makes as to understand how to inherit the feature from the base class to derived class is class inheritance type or reusable techniques.
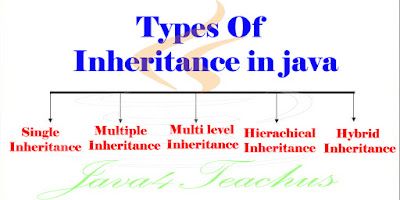
They are five types of inheritance they are
They are five types of inheritance they are
1) Single inheritance.
2) Multi level inheritance.
3) Hierarchical inheritance.
4) Multiple inheritance.
5) Hybrid inheritance.