Super Keyword in java
Super is a keyword or reference variable in java which is used to refer the parent object. Super is an implicit keyword which is created by JVM for each and every program during compile time to playing the 3 important role. They are:
- Super keyword at data members or variable level.
- Super keyword at Method level.
- Super keyword at Constructor Level.
Purpose Of Super Keyword
Syntax
Super Keyword at Data Member/Variable Level.
Whenever the derived class inherit the base class data members, there is a possibility that base class data members are similar to the derived class data members and JVM gets ambiguity.
In Order to differentiate between base class data members and derived class data members, in the context of derived class and base class data members must be preceded by super keyword.
Syntax
If we do not write a super keyword before base class data members then that data members is consider by JVM like as derived class data members and base class data members will be hidden.
Program:1
class BaseClass
{
int a;
}
class DerivedClass extends BaseClass
{
int a,b;
void set(int x,int y)
{
super.a=x;
this.a=y;
}
void add()
{
b=super.a+this.a;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println("value of Baseclass :" + super.a);
System.out.println("value of Derivedclass :" + this.a);
System.out.println("Summ :"+b);
}
}
class BaseDerivedClassEx
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DerivedClass d=new DerivedClass();
d.set(10,20);
d.add();
d.display();
}
}
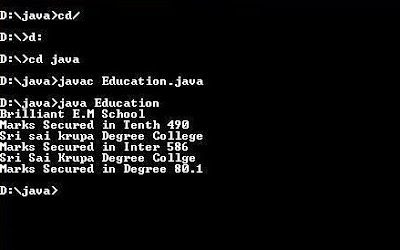
Output
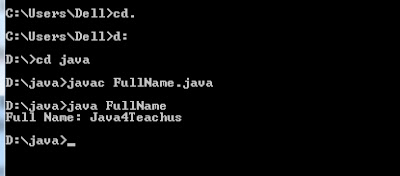
Program :2
class First
{
String name="Java4";
}
class SecondName extends First
{
String name="Teachus";
void display()
{
String merge=super.name+name;
System.out.println("Full Name: "+ merge);
}
}
class FullName
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SecondName s=new SecondName();
s.display();
}
}
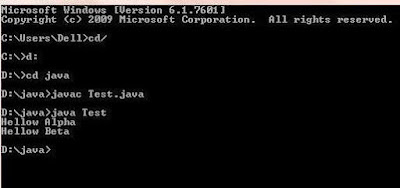
Output