Variable's & Constant's
Definition: "A variable is an identifier that can denotes the storage location used to store a data value in the primary memory of a computer". A variable may take different values in different times during the execution of the a program.
In Java, variable are the names of storage locations that specify the location of a variable. After designing it uses for suitable variable names, we must declare them to the compiler. They are:
➤ A variable name can be chosen by the programmer in a meaningful way, so it is reflected as like a what we represents in the programs.
➤ It tells the compiler what is the variable names.
➤ It specify the what type of data that variable will hold.
➤ The place of declaration in the program to decide the scope of the variable .
A variable must be declared before it is used in the program. It can be used to store a value of any data type. After declaration of variables we must be end with semicolon other wise we get error's in the program.
Syntax:- Datatype variable 1, variable 2 ;
Example:- int ID NO;
float percentage;
double PI;
char grade;
Ex:- 0.011 - 0.25 123.45
The above numbers are shown in decimal notations.
➤ Character Constants :- A single character constant contain single character enclosed within a pair of single quote marks. Some of the examples are 'L','U','C','K','Y' .
➤ String Constant :- A single constant is a sequence of character enclosed between double quotes. The characters may be alphabets, digits, special characters and blank spaces.
Ex:- "Hello Lucky","20", "Java", "A" .
Constant's
Definition: Constants are fixed values that cannot be changed during the execution of a program. Java constants are discussed below and they are classified into 2 types. They are :
1.Numeric Constants.
a. Integer Constants b. Real Constants
2.Character Constants.
a. Character Constants b. String Constants
➤ Integer Constants:- An Integer Constants refers to a sequences of digits.There are three types of integers, namely, decimal integer, octal integer and hexadecimal integer.
- Decimal integer consists of a set of digits like 0 to 9 which is preceded by an optical minus sign.
- An octal integer constant consist of any combination of digits from the set of 0 to 7 with a leading of 0.
- A sequence of digits preceded by OX is considered as Hexadecimal integer.
Ex:- 0.011 - 0.25 123.45
The above numbers are shown in decimal notations.
➤ Character Constants :- A single character constant contain single character enclosed within a pair of single quote marks. Some of the examples are 'L','U','C','K','Y' .
➤ String Constant :- A single constant is a sequence of character enclosed between double quotes. The characters may be alphabets, digits, special characters and blank spaces.
Ex:- "Hello Lucky","20", "Java", "A" .
Purpose Of Datatypes
In the software industry, we have to use different types of data types in the real-industry which is shown as a practically to the new learner of Java.
The purpose of data types in every programming language allocates the
sufficient amount of memory space to the input of the program in the main
memory of the computer. In any programming language data types are classified into 3 types:
- Fundamental data type
- Derived data types
- User / Programmer defined data types
1.Fundamental data types
These data types are developed by language developers and available as a part of languages and whose role is to store single value and they never allow to store "multiple value of same types".
Example 1:- int a=10; // valid

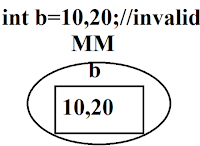
The above example 2 is invalid, Because it can stored only one value but more than two values in variable.
2.Derived data types
In every
programming language the concept of arrays comes under derived data types.But in the java we call array is also known as Length by using [ ] .
The role
of derived data types is to store “multiple value of same type”, But it cannot be store
“multiple value of different types”. Which is shown in the below Example 2 .
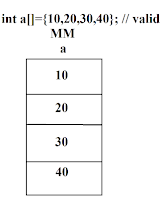
Example 1 :- int a[ ] = {10,20,30,40}; // valid
The above example 2 is in valid, Because it can be stored " Multiple values of different data types".
3.Programmer/User defined data type
Programmer defined datatype is mainly is used stores the "Multiple value of Same data types & Different data types" and also "Both type of data types" is also known as programmer defined or user defined data type .
In Java programming language we can store the multiple value of same or different data types, By using these concepts in java like " classes, Interfaces, Enumerations " etc...
Example 2 :- Employee e = new Employee ( ) ;
➤➤➤ Fundamental Data types In java



Super keep it bro .this is sreenath
ReplyDeletethank you sreenath.
ReplyDelete